Chemical products
-

Morpholine
Morpholine, a nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compound with the chemical formula C₄H₉NO, is a colorless liquid with a mild ammonia-like odor. Possessing unique physical and chemical properties, morpholine finds extensive applications in various industries. It serves as a solvent, cleaning agent, chemical intermediate, and a crucial precursor in the synthesis of other compounds. Properties of Morpholine: Applications…
-

Sodium cyanide
Sodium cyanide, a highly toxic white crystalline solid with the chemical formula NaCN, is a compound composed of sodium (Na) and cyanide (CN). Due to its release of cyanide ions (CN-) in water, this compound is extremely poisonous. Cyanide ions interfere with the function of cellular enzymes involved in cellular respiration, causing toxicity. Industrial Applications…
-

Dimethyl disulfide
Dimethyl disulfide (DMDS), also known as bis(methylthio)methane, is an organic sulfur compound with the chemical formula CH3SSCH3. It exists as a colorless liquid with a strong, unpleasant garlic-like odor. DMDS finds diverse applications in various industries due to its unique properties and reactivity. Physical and chemical characteristics Melting Point: -92°C (-134°F) Boiling Point: 115.6°C (240°F)…
-

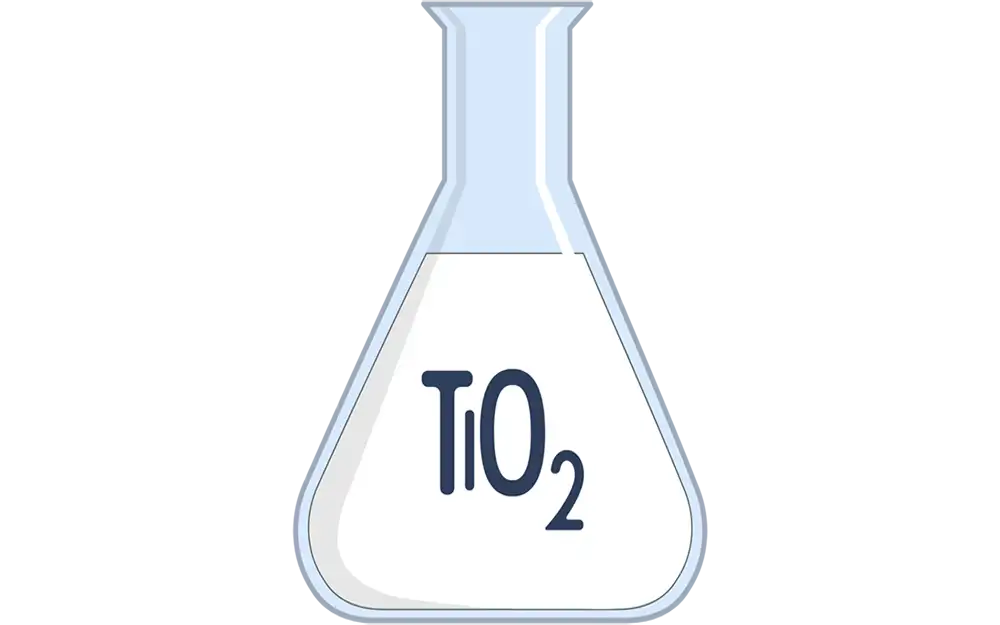
Titanium dioxide
Titanium dioxide (TiO2), with its deceptively simple chemical formula, unlocks a world of remarkable applications. This naturally occurring mineral exists as a white, odorless powder and finds extensive use in diverse industries due to its unique properties. From coloring our world to safeguarding our health, titanium dioxide plays an indispensable role in modern life. Delving…
-

Polyvinyl alcohol
Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), with its simple chemical formula (C2H4O)n, stands as a versatile synthetic polymer that has captivated the attention of various industries. This water-soluble polymer presents itself as a white or cream-colored powder, readily soluble and capable of withstanding temperatures up to 230 degrees Celsius before decomposition. PVA’s unique properties, including biodegradability, solvent resistance,…
-

Potassium Carbonate
Potassium carbonate, also known as potash or pearl ash, is a versatile inorganic compound with the chemical formula K2CO3. It exists as a white, crystalline solid that readily dissolves in water, forming a strongly alkaline solution. Due to its unique properties, potassium carbonate finds extensive applications in various industries. Names and Physical Properties Potassium carbonate…
-

Ortho dichlorobenzene
Ortho-dichlorobenzene (ODCB), with the chemical formula C6H4Cl2, is one of the isomers of dichlorobenzene that finds extensive applications in various industries due to its unique properties. It is a colorless liquid with a pleasant odor, soluble in water, and miscible with many organic solvents. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive overview of ortho-dichlorobenzene,…
-

formic acid
Formic acid, with the chemical formula HCOOH, is the simplest carboxylic acid and finds extensive applications in various industries due to its unique properties. It occurs naturally in some living organisms and is also synthesized through chemical methods. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive overview of formic acid, including its properties, production, applications,…
-

Ammonium persulfate
Ammonium persulfate, with the chemical formula (NH₄)₂S₂O₈, is a white crystalline inorganic compound that serves as a potent oxidizing agent in various industries. Its high solubility in water and thermal stability make it a valuable material. In this article, we will delve into the properties, production, and applications of ammonium persulfate. Physical and chemical properties…
-

Polyelectrolyte
Polyelectrolyte is an amazing molecule that plays an essential role in water purification and clarification by coagulation of suspended and colloidal particles. Water, the elixir of life, is constantly exposed to various contaminants, including suspended and colloidal particles. These microscopic particles, invisible to the naked eye, can impart unpleasant color, odor, and taste to water,…
-

molecular sieve
Molecular sieve is a group of porous inorganic materials with a regular crystalline structure. Due to their high specific surface area and ability to selectively adsorb specific molecules, they find wide application in a diverse range of industrial and scientific fields. History of Molecular Sieves The history of molecular sieves dates back to ancient times,…
-

Silica gel (H and WS)
Silica gel, a porous, non-toxic desiccant composed of silicon dioxide (SiO2), is widely recognized for its exceptional moisture absorption capabilities. Its highly porous structure provides an extensive surface area, making it an ideal adsorbent for water and water vapor. Available in various forms, including beads, powder, sheets, and blocks, silica gel finds applications across a…
-

lithium bromide
Lithium bromide (LiBr) is a remarkable inorganic compound that finds applications in various fields due to its unique properties. It is particularly well-known for its exceptional moisture absorption capabilities, making it a valuable desiccant in numerous applications. Key Properties of Lithium Bromide Physical Properties Safety Considerations LiBr is non-toxic but should be handled with care…
-

Polyaluminium Chloride
Polyaluminium chloride (PAC), also known as PACl, is a highly effective coagulant widely used in water and wastewater treatment applications. It is a versatile and efficient alternative to traditional coagulants like aluminum sulfate and ferric chloride, offering numerous advantages in terms of performance, cost-effectiveness, and environmental impact. Advantages of Polyaluminium Chloride (PAC) High Efficiency PAC…
-

Activated Alumina
Activated alumina, also known as activated aluminum oxide, is a highly porous and adsorbent material derived from the dehydroxylation of aluminum hydroxide (Al(OH)3). Its exceptional porous structure provides an extensive surface area, exceeding 200 square meters per gram, making it a valuable material for various applications, including moisture adsorption, filtration, and catalysis. Key Properties of…
-

Activated Carbon
Activated carbon also known as activated charcoal, is a porous form of carbon that has been processed to increase its surface area and porosity. This extensive surface area, typically exceeding 3,000 square meters per gram, makes activated carbon an exceptional adsorbent for various applications, including purification, filtration, and catalysis. Key Properties of Activated Carbon Applications…